
Who is it for?
Surgical treatment of obesity is intended for people between 18 and 60 years old with:
- class II obesity, i.e. with the body mass index BMI ≥35, and a concomitant disease, such as hypertension, type 2 diabetes, lipid disorders, coronary heart disease or joint diseases due to overload
- class III obesity, so-called ‘morbid obesity’ i.e. with the body mass index BMI ≥40
SURGICAL TREATMENT OF OBESITY
prof. dr hab. n. med. Tomasz Rogula
[arve url=”https://zabiegidavinci.pl/wp-content/uploads/2020/08/prof-rogula-bariatria-en-720p-5.mp4″ align=”center” promote_link=”no” thumbnail=”6382″ title=”Chirurgiczne leczenie otyłości – zabiegi bariatryczne w Szpitalu na Klinach” description=”Operacyjne leczenie otyłości – operacje zmniejszania żołądka” upload_date=”2020-02-06T12:49:03Z” maxwidth=”1280″ aspect_ratio=”16:9″ mp4=”https://zabiegidavinci.pl/wp-content/uploads/2020/08/prof-rogula-bariatria-en-720p-5.mp4″ /]
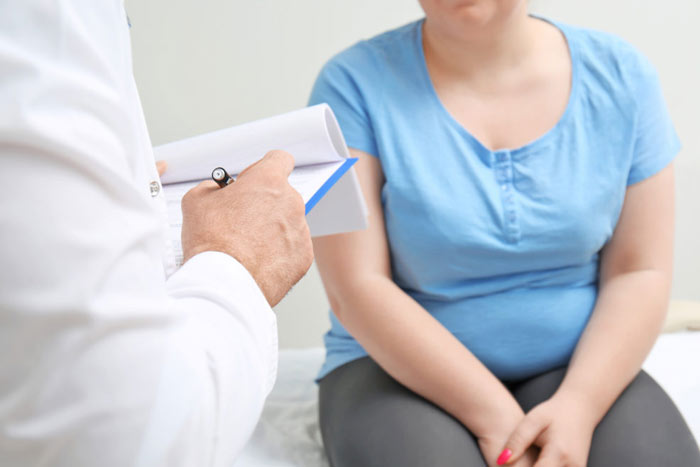


Contraindications to the procedure
- Cancer
- Gastrointestinal inflammatory diseases
- Mental disorders
- Endocrine diseases
- Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease
- Addiction to alcohol or drugs
- Pregnancy
How do we treat obesity?
At the Krakow-based Na Klinach Neo Hospital patients are cared for by a multidisciplinary team of specialists comprised of:
- a consultant: bariatric surgeon;
- a cardiologist and GP;
- a pulmonologist;
- dietitian;
- a psychologist;
- a physiotherapist.
The process of treatment begins with a two-stage pre-assessment programme consisting of specialist consultations and laboratory and diagnostic tests. Based on its outcome, the doctor will choose the method of weight loss, e.g. a conservative procedure or surgical treatment of obesity. The actual method is dependent on the age and sex of the patient, the type of obesity and the possible presence of accompanying diseases. Before the planned procedure, each patient is provided with comprehensive care for a period of approx. 4-6 months the purpose of which is to cause a loss of body weight of 10% (alternatively 10 kg).
Stages of surgical obesity treatment
- • STAGE I – PRE-ASSESSMENT PROCEDURE – CONSERVATIVE TREATMENT
- STAGE II – PRE-ASSESSMENT PROCEDURE – OPERATION
Surgical treatment of obesity should always be preceded by conservative treatment with the use of diet and pharmacotherapy; it is only after its completion that the next step, which is the surgical procedures, be started. The full assessment of fitness for the surgical treatment involves a number of necessary medical consultations and examinations.
- consultation with the consultant bariatric surgeon
The purpose of the consultation is to assess the patient’s general state of health and establish the basis for surgical treatment of obesity. During the visit the doctor will perform a gastroscopy and arrange for other necessary examinations and consultations. It is only based on their results that the patient can be referred for surgical treatment.
- consultation with a cardiologist
During the consultation, the doctor will check the general state of the cardiovascular system, perform an echocardiogram and exercise ECG. In addition, they will rule out or confirm the presence of any diseases that accompany obesity, such as hypertension, which increase the risk of haemorrhagic stroke or myocardial infarction.
- consultation with a psychologist
Prior to surgical treatment of obesity, each patient will be seen by a psychologist who will assess the patient’s determination and readiness for the introduction of some radical changes in their lifestyle. The psychologist will first of all check the level of motivation as well as the patient’s awareness of the challenges involved in limiting food intake both before and after the surgery.
- consultation with a dietitian
The dietitian’s role will be to analyse the patient’s daily diet based on their dietary diary. Additionally, the specialist will perform an analysis of the body weight and assess the current diet. If necessary, they will develop an optimal dietary programme to reduce body weight and balance the daily diet. In the case of a planned operation, the consultation also serves the purpose to prepare the patient for the surgery and to plan an appropriate diet after the operation.
- examinations – body weight measurement and other tests to identify any possible concomitant diseases, such as diabetes, hypertension, kidney diseases, peptic ulcer or reflux disease, as well as immunological disorders that are typically found in obese patients.
Standard examinations
- Echocardiography
- Cardiac stress test according to the cardiologist’s instructions
- ECG
- Chest X-ray
- Abdominal ultrasound scan
- Doppler ultrasound of lower limb veins
- Spirometry test
- Sleep apnea test (polysomnography)
- Body composition analysis
- Blood count
- Glucose tolerance test (3-hour OGTT)
- Biochemical tests: creatinine, urea, sodium, potassium, bilirubin, AST, ALAT and lipid profile
- HbS
- Level of anti-HCV antibodies
During conservative treatment, each patient is under constant care of a bariatric surgeon, psychologist and dietitian. Additionally, dietary recommendations are printed out and a body composition analysis is carried out twice. Telephone contact is also available for matters that do not require direct consultation. We also provide our patients with the option of an email contact at least once a week.
Before the procedure, each patient is taken under the care of a surgeon and an anaesthesiologist, and additionally receives necessary materials supporting them in their struggle to lose extra weight.
Surgical methods used to treat obesity
I . Gastric band
Placing an adjustable gastric band is one of the methods of surgical treatment of obesity. This operation can be performed on practically every healthy person with obesity that is not able to permanently and effectively lose weight. Nevertheless, adjustable gastric band is recommended for people in whom more advanced surgical procedures such as gastric resection or gastric bypass, carry a risk of complications or are not possible due to concomitant diseases. The procedure includes the care of a bariatric surgeon as well as consultations by a dietician and a psychologist, also post-hospitalisation.
What does the procedure involve?
The operation involves placing an adjustable silicone band around the top portion of the stomach, which in effect divides it into two parts. It can be adjusted to regulate the rate of passage of food to further parts of the digestive tract. Depending on how tight the band is adjusted, more or less food can be taken, and the patient only eats the amount that fits in the stomach pouch that is created by the band. This method makes it possible to adjust the rate of weight loss but requires a special semi-liquid diet. The band can be removed at any time.
Preparation for the procedure:
Laboratory tests:
- blood count, blood group and Rh factor
- basic biochemical tests (sodium, potassium and glucose)
- ECG
other examinations as ordered by the physician
Average length of hospital stay: up to 3 days
II. Sleeve gastrectomy
This method is especially recommended for patients whose BMI is 40 or 35 and who have secondary diseases associated with obesity, such as hypertension, sleep apnea syndrome or degenerative joint disease. The procedure involves resection of a part of the stomach so that only about 30% of its volume remains. In effect, after sleeve gastrectomy the patient is not able to take large amounts of food at a time, which results in spontaneous weight loss. The procedure includes the care of a bariatric surgeon as well as consultations by a dietician and a psychologist, also post-hospitalisation.
What does the procedure involve?
The operation consists in a laparoscopic partial excision of the stomach so that the remaining portion can hold 100-150 ml of food. In addition, the appetite-stimulating hormone ghrelin is no longer secreted. After the surgery patients lose about 60% of their body weight during a year; also after the surgery, it is very important to follow a diet in which only finely chopped foods can be consumed in much smaller portions than before the surgery. The procedure permanently reduces the volume of the stomach and is irreversible.
Preparation for the procedure:
Laboratory tests:
- blood count, blood group and Rh factor
- basic biochemical tests (sodium, potassium and glucose)
- ECG
- other examinations as ordered by the physician
Standardowa długość pobytu w szpitalu: do 5 dni
III. Gastric bypass surgery
The treatment is especially recommended for people who suffer from type 2 diabetes and other metabolic syndromes in addition to obesity. The method is characterised by very high effectiveness for weight loss due to the fact that it significantly affects the processes of absorption and digestion of food and the normalisation of the metabolic processes, which may in effect lead to reversal of diabetes. The procedure includes the care of a bariatric surgeon as well as consultations by a dietician and a psychologist, also post-hospitalisation.
What does the procedure involve?
The operation involves cutting the stomach to produce a small pouch with a volume of approx. 50 ml, which is then connected to the small intestine. The reduced stomach prevents binge eating and the food goes directly into the small intestine bypassing the duodenum and approx. 150 cm of the jejunum. Therefore, the operation is not only restrictive in terms of reducing the volume of food taken but also limits absorption of food. After the operation, the patient must follow a special diet and take vitamins in order to lose weight in a controlled way.
Preparation for the procedure:
Laboratory tests:
- blood count, blood group and Rh factor
- basic biochemical tests (sodium, potassium and glucose)
- ECG
- other examinations as ordered by the physician
Average length of hospital stay: up to 5 days

 +48 785 054 460
+48 785 054 460